How to deploy Trial Networks
You first create a descriptor, and then publish it to the TNLCM The descriptor is a YAML file that describes the components, their configurations, and the relationships between them.
Then you use the TNLCM to deploy the Trial Network based on that descriptor.
TNLCM Overview
Trial Network Lifecycle Manager (TNLCM) is a tool designed to manage the lifecycle of trial networks. Developed in Python, it automates the creation, deployment and management of temporary or test networks, streamlining the process of experimentation and validation in network development projects.
⚠️ Currently, TNLCM is mainly operated through its Swagger UI
You can explore all available functionalities and understand how it works in the TNLCM usage page.
A dedicated frontend interface is under development to enable managing trial networks directly from a user-friendly web dashboard.
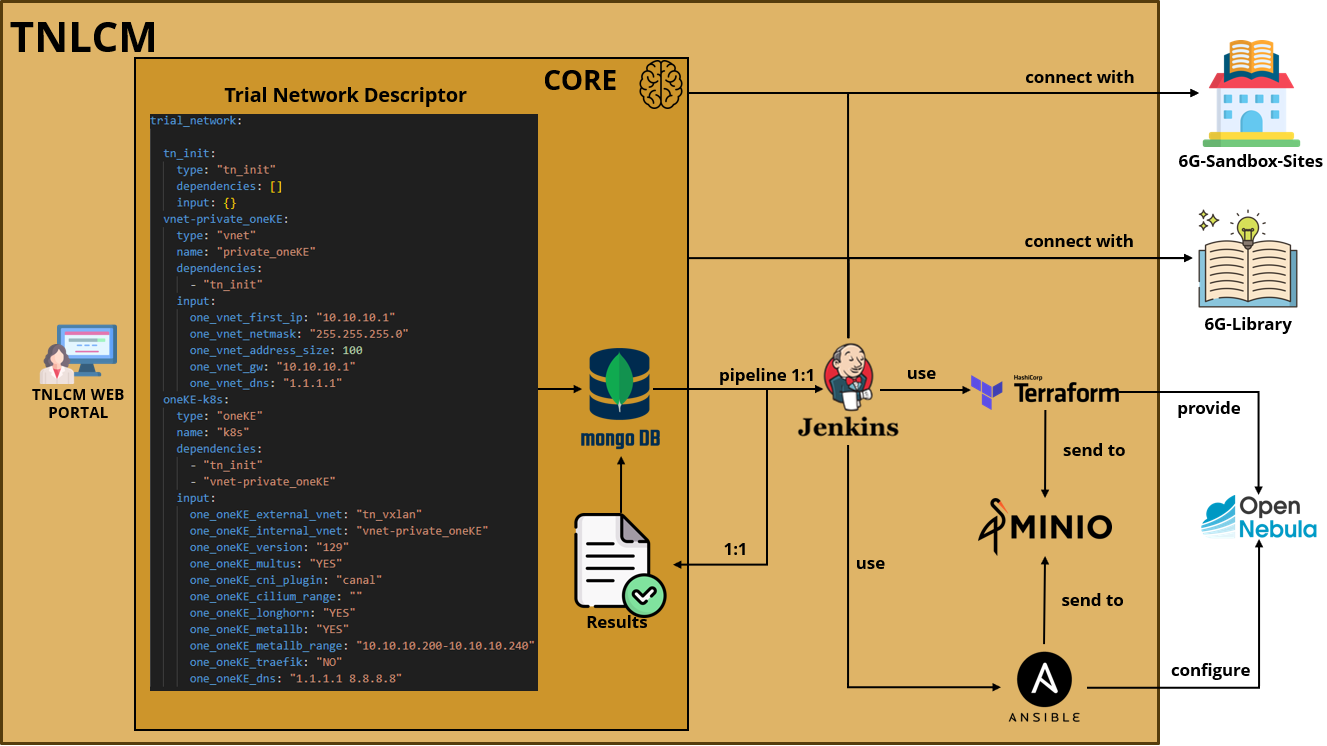
Overview of TNLCM and 6G-Library implementation
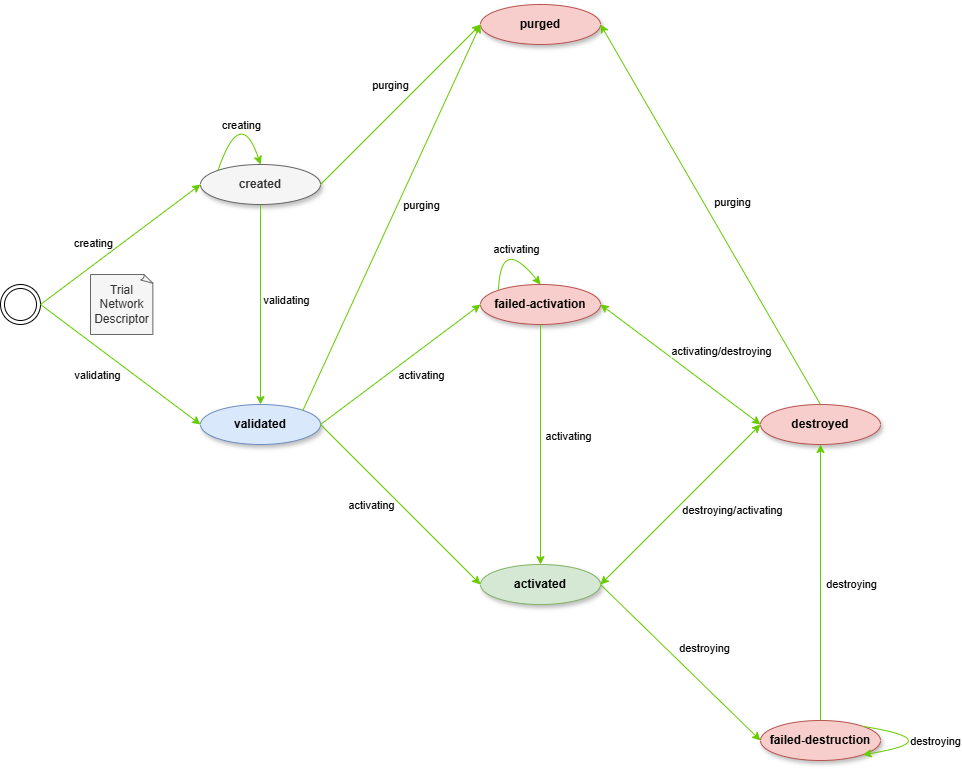
State Machine
TNLCM is a state machine that allows the automation of component deployment. Green indicates what is implemented and red indicates what is in the process of implementation.
States
- activated: the trial network is deployed in OpenNebula and ready to use.
- created: the trial network descriptor is created but not yet validated.
- destroyed: the trial network deployment is removed from OpenNebula and ready for deploy again.
- failed-activation: the trial network deployment failed. It is waiting for the user to try again.
- failed-destruction: the trial network deployment removal failed. It is waiting for the user to try again.
- purged: all the information about the trial network is removed from the database.
- validated: the trial network descriptor is created and validated. It is ready to be deployed in OpenNebula.
Transitions
- initial-state → created: create a trial network descriptor that not validated yet. It allows save the descriptor for further editing at a later time.
- initial-state → validated: create and validate a trial network descriptor in the same step. It check if the descriptor can be deployed.
- created → created: edit the trial network descriptor.
- created → validated: apply validation to the trial network descriptor.
- created → purged: remove all the information about the trial network in database.
- validated → purged: remove all the information about the trial network in database.
- validated → activated: activate the trial network. It deploys the trial network in OpenNebula.
- validated → failed-activation: trial network deployment failed. It is waiting for the user to try again.
- failed-activation → failed-activation: retry the trial network deployment and it fails again.
- failed-activation → activated: retry the trial network deployment and it is successful.
- failed-activation → destroyed: remove the trial network deployment from OpenNebula and ready for deploy again.
- activated → destroyed: remove the trial network deployment from OpenNebula and ready for deploy again.
- activated → failed-destroyed: trial network deployment removal failed. It is waiting for the user to try again.
- destroyed → purged: remove all the information about the trial network in database.
- destroyed → failed-activation: retry the trial network deployment and it fails.
- destroyed → activated: retry the trial network deployment and it is successful.
- failed-destruction → destroyed: retry the trial network deployment removal and it is successful.
- failed-destruction → failed-destruction: retry the trial network deployment removal and it fails again.